Artificial intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science that aims to create intelligent machines that can learn, reason, and perceive their environment like humans. AI significantly impacts various industries by automating and improving processes, enhancing decision-making, and enabling new products and services. AI significantly impacts finance by transforming how financial institutions operate and serve their customers. AI automates financial processes, makes predictions, and improves decision-making. For example, AI is used in trading to identify patterns and trends in financial data and make trades autonomously. This is particularly useful in high-frequency trading, where speed is critical. AI is also used to identify fraud in financial transactions, reducing the risks associated with financial crime. In addition, AI-powered chatbots provide customer service and personalized financial advice, improving the customer experience. One of the most significant impacts of AI on finance is its ability to analyze vast amounts of data quickly and accurately. AI algorithms can research financial data from multiple sources, identify patterns, and predict trends. This allows financial institutions to make better investment decisions and manage risk more effectively. AI is also used to develop credit scoring models that analyze an individual's credit history, income, and other factors to assess their creditworthiness accurately.

II. Applications of AI in Finance
a. Automated trading and portfolio management
Automated trading and portfolio management involves using AI and machine learning algorithms to automate investment decisions and manage investment portfolios. Automated trading involves using algorithms to analyze market data and make trades autonomously based on predefined rules and parameters. Portfolio management uses AI to diagnose and manage investment portfolios to optimize performance and minimize risk. AI-powered portfolio management systems use algorithms to analyze investment data, identify trends, and provide personalized investment advice. Automated trading and portfolio management can reduce costs, increase efficiency, and improve investment performance by eliminating human biases and emotions. However, there are risks associated with relying solely on AI for investment decisions, such as the potential for technical errors and the lack of human oversight.
b. Fraud detection and prevention
Fraud detection and prevention is an essential application of AI in finance. AI algorithms can analyze large volumes of financial data and identify patterns of fraudulent activity, such as unusual spending patterns, suspicious transactions, and account takeover attempts. AI-powered fraud detection systems can also learn and adapt to new fraud patterns over time, improving their accuracy and effectiveness. In addition, AI-powered authentication and verification systems can help prevent fraud by verifying the identity of customers and ensuring that only authorized individuals have access to financial accounts. AI-based fraud detection and prevention systems can reduce financial losses and enhance customer trust, but they also require careful monitoring and management to avoid false positives and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
c. Credit scoring and underwriting
AI is transforming the way financial institutions assess creditworthiness through automated underwriting. AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of data, including credit history, income, and other factors, to determine the creditworthiness of individuals and businesses accurately. This allows for faster and more accurate credit decisions and personalized loan products. By automating the underwriting process, financial institutions can reduce costs and increase efficiency while minimizing the risk of human error and bias. However, there are concerns about the potential for algorithmic bias and the need for transparency and accountability in credit decision-making.
d. Customer service and chatbots
AI-powered chatbots are changing customer interactions with financial institutions. Chatbots can provide personalized assistance and answer customer inquiries about account balances, transaction history, and other financial services. With 24/7 availability and fast response times, chatbots can reduce wait times and improve customer experience. Chatbots can also automate routine tasks such as updating account information, processing payments, and providing loan information. AI algorithms can analyze customer interactions and learn from them, improving the accuracy and effectiveness of chatbots over time. However, there are also concerns about the limitations of chatbots and the importance of balancing automated services with human support for complex customer needs.
e. Personalized financial advice and recommendations
AI transforms financial advice by providing personalized recommendations and insights for individuals and businesses. AI algorithms can analyze financial data, including spending patterns, investment portfolios, and credit history, to identify opportunities for savings and investment. With personalized financial advice, individuals and businesses can make informed financial decisions that align with their goals and objectives. AI-powered financial advisors can also provide customized investment recommendations, such as asset allocation and diversification strategies. However, there are also concerns about the potential for algorithmic bias and the need for transparency and accountability in financial advice. AI in financial advice should be carefully monitored and regulated to ensure that it benefits consumers and the broader financial system.

III. Benefits of AI in Finance
a. Improved efficiency and cost savings
With automation, AI can streamline financial processes, including account opening, loan processing, and fraud detection, reducing the need for human intervention and manual processing. This can result in significant cost savings for financial institutions while improving accuracy and speed. AI algorithms can also optimize investment portfolios, reducing transaction costs and maximizing returns. In addition, AI-powered chatbots can handle routine customer inquiries, reducing the need for human customer service representatives and improving the overall customer experience. However, there are also concerns about the potential for job displacement and the need to ensure that the benefits of AI are distributed equitably across society.
b. Enhanced accuracy and reduced errors
AI is reshaping the financial industry by enhancing accuracy and reducing errors. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of financial data quickly and accurately, reducing the risk of human error and bias. This is particularly important in areas such as fraud detection, credit scoring, and investment management, where accuracy is critical to financial institutions' success and their customers' well-being. AI-powered systems can also learn and adapt to new patterns and trends, improving accuracy. By reducing errors and improving accuracy, AI can improve the quality of financial services and reduce the risk of financial losses for individuals and businesses.
c. Greater scalability and accessibility
Scalability and accessibility are two significant benefits of using AI in the financial industry. With AI, financial institutions can scale their operations to handle increasing volumes of data and transactions without significantly increasing costs or resources. This means that financial institutions can serve more customers, expand their offerings, and improve their competitiveness in the market. Additionally, AI-powered financial services can be accessed anytime, anywhere, through mobile and online platforms, making financial services more accessible to underserved communities and individuals. This can lead to greater financial inclusion, allowing more people to access financial services and improve their financial well-being.
d. Better risk management and decision-making
AI provides financial institutions with better risk management and decision-making capabilities. By analyzing large volumes of data, AI algorithms can identify patterns and trends that may indicate potential risks and threats, enabling financial institutions to take proactive measures to manage risks and prevent losses. AI can also provide valuable insights that support better decision-making, such as identifying investment opportunities or optimizing portfolio diversification. With AI-powered risk management and decision-making tools, financial institutions can make more informed decisions and reduce the risk of financial losses. However, it is crucial to ensure that AI algorithms are transparent, explainable, and free from bias and to balance automated decision-making with human oversight and intervention where necessary.

IV. Challenges and Risks of AI in Finance
a. Lack of transparency and accountability
One of the critical challenges associated with using AI in finance is the Lack of transparency and accountability. Financial institutions must ensure that their AI systems are transparent and explainable, with clear documentation of the data and algorithms used to make decisions. This is particularly important in credit scoring and investment management, where decisions can significantly impact individuals and businesses. There are also concerns about the potential for algorithmic bias and discrimination, particularly in areas such as lending and insurance. Implementing appropriate governance and oversight mechanisms is essential to ensure that AI systems are developed and deployed ethically and responsibly.
b. Bias and discrimination in data and algorithms
AI in finance raises concerns about bias and discrimination in data and algorithms. AI algorithms are only as unbiased as the data they are trained on, and if the data reflects systemic biases, the resulting algorithms will also be biased. This can result in discrimination against certain groups, such as minorities or women, in areas such as credit scoring and insurance underwriting. It is essential to develop and deploy AI systems to minimize the risk of bias and discrimination, such as by ensuring diversity and inclusivity in the data used to train algorithms and implementing appropriate governance and oversight mechanisms.
c. Cybersecurity threats and hacking risks
Another significant challenge associated with using AI in finance is the increased cybersecurity threats and hacking risks. Financial institutions hold vast amounts of sensitive financial and personal data, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals. AI also introduces new vulnerabilities, such as the potential for adversarial attacks, where malicious actors manipulate AI systems to make incorrect decisions or predictions. Financial institutions must implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect against these threats, such as encrypting data, implementing multi-factor authentication, and continuously monitoring and updating security systems. It is also essential to ensure that AI systems are developed and deployed securely and that appropriate measures are in place to detect and respond to cybersecurity incidents.
d. Job displacement and economic inequality
The increasing use of AI in finance also raises concerns about job displacement and economic inequality. AI can automate many routine and repetitive tasks, such as data entry and transaction processing, potentially leading to job losses for human workers. This could exacerbate economic inequality, particularly for those with low-skilled or routine jobs. It is essential to ensure that the benefits of AI are shared more broadly and that workers are equipped with the skills needed to thrive in an AI-driven economy. This could include investing in education and training programs that help workers develop the necessary skills to work alongside AI systems and in areas where human judgment and creativity are still necessary.
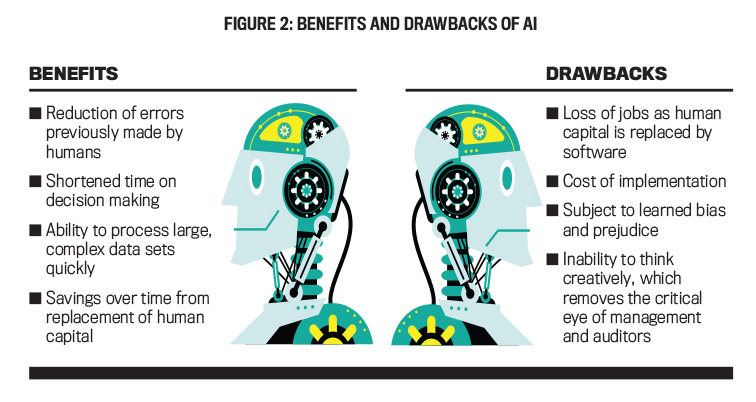
V. Future of AI in Finance
Emerging trends, innovations, and regulatory and ethical considerations characterize the future of AI in finance. One emerging trend is using natural language processing (NLP) and sentiment analysis to improve customer service and personalize financial advice. This allows financial institutions to better understand their customers' needs and preferences and tailor their offerings accordingly. Another trend is the use of explainable AI, which improves transparency and accountability by allowing financial institutions to understand how AI systems make decisions. However, regulatory and ethical considerations also play an essential role in shaping the future of AI in finance. The use of AI in finance is subject to various regulations and standards, including the EU's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) in the US. It is also essential to ensure that AI systems are developed and deployed ethically and responsibly, considering potential risks and impacts on society. This includes ensuring that AI systems are transparent, explainable, and bias-free and that appropriate governance and oversight mechanisms are in place. The potential impact of AI on the financial industry and society as a whole is significant. AI has the potential to revolutionize the financial sector by improving efficiency, accuracy, and decision-making, as well as enhancing customer experience and personalization. However, it is also essential to consider potential unintended consequences, such as job displacement, economic inequality, and the potential for algorithmic bias and discrimination.

VI. Conclusion
In conclusion, the future of AI in finance is characterized by emerging trends and innovations, as well as regulatory and ethical considerations. While AI can transform the financial industry, ensuring it is developed and deployed responsibly and ethically is essential, considering potential risks and impacts on society. By doing so, the financial sector can leverage the benefits of AI while minimizing its possible negative consequences.





